Policy Briefs: Public Financing for Nutrition in Bihar
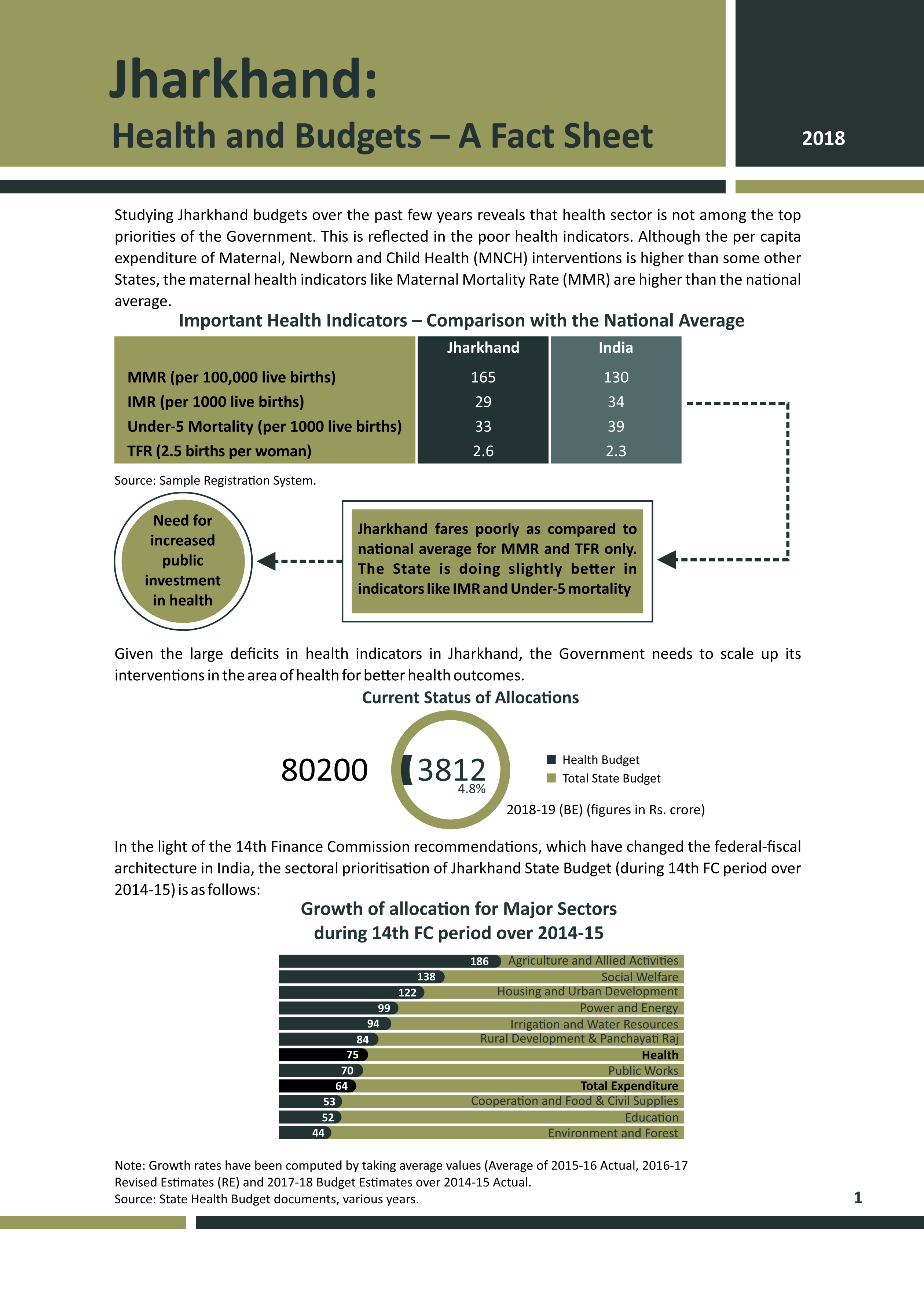
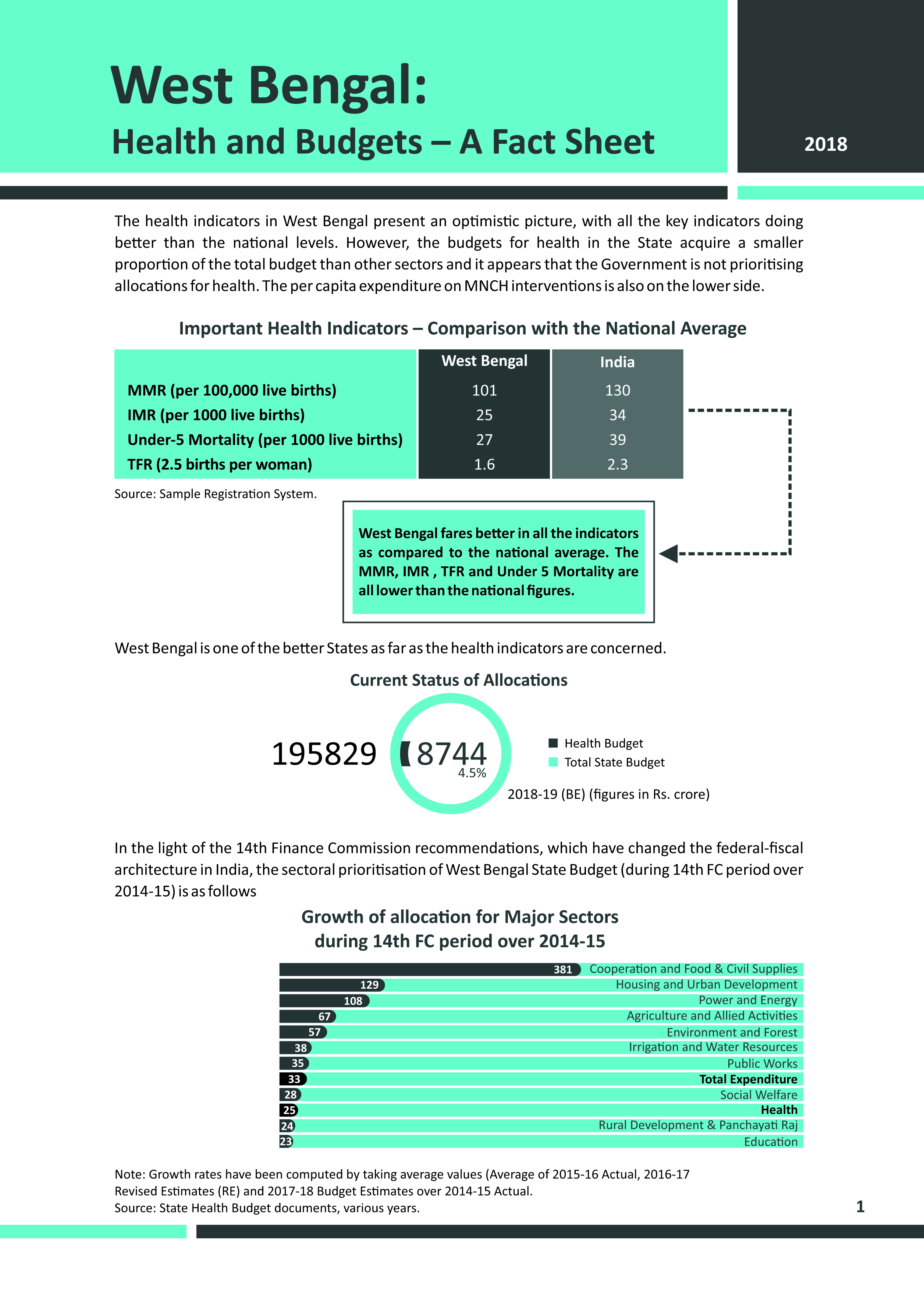
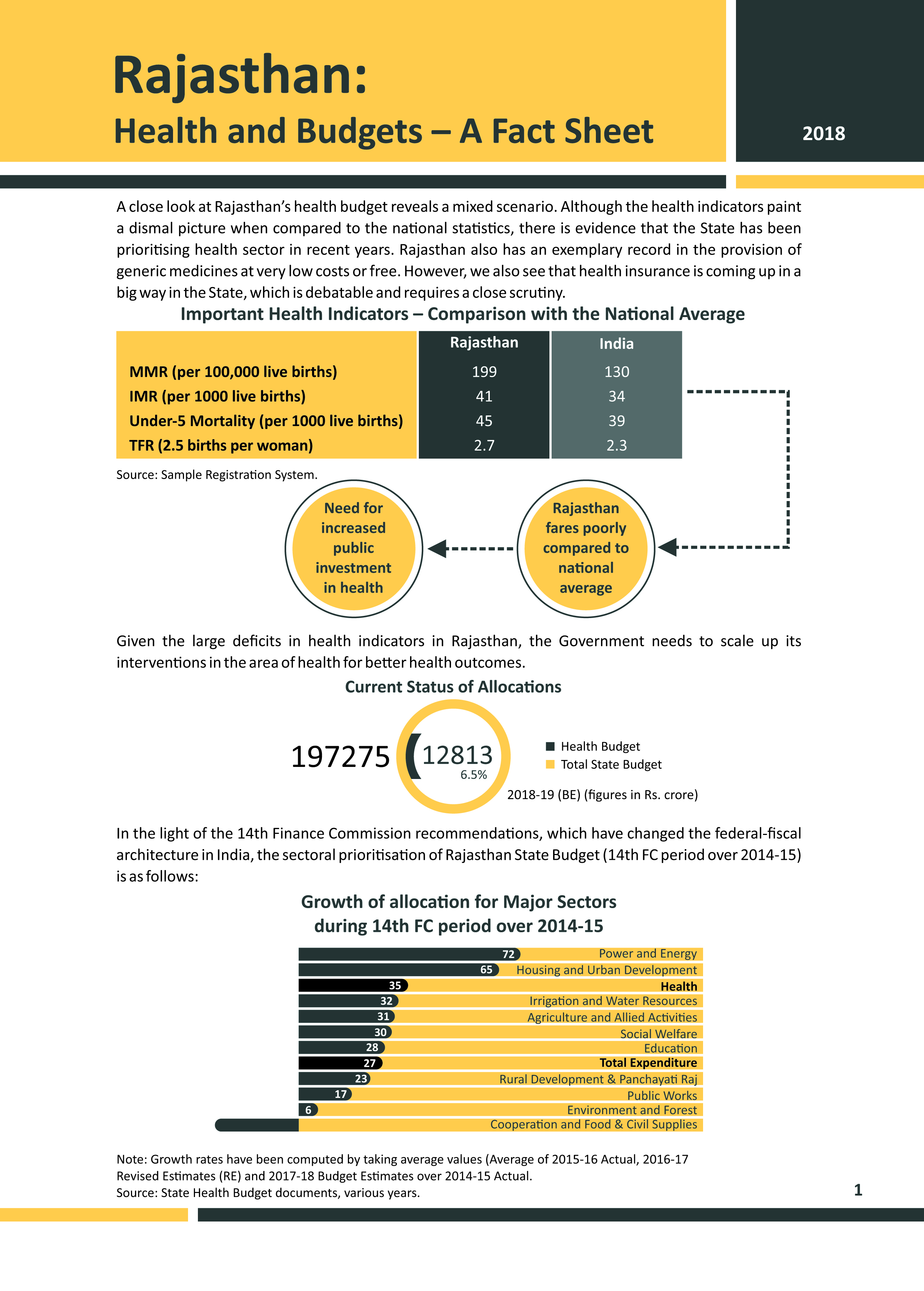
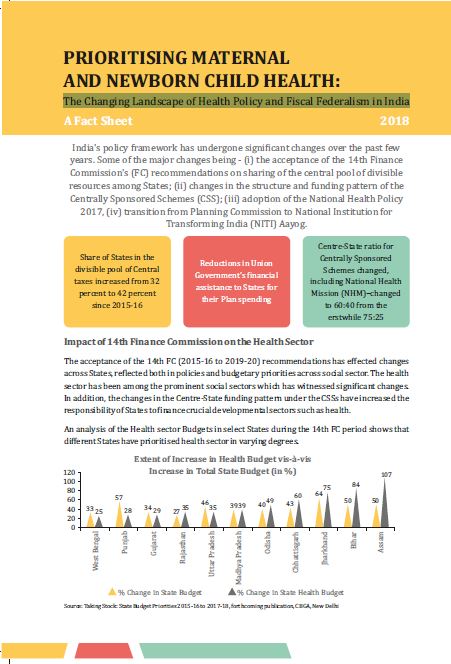
Bihar has made noticeable improvements in nutritional outcomes over the last decade, with stunting among children under five years of age falling from 56 % in 2005-06 to 48 % in 2015-16 (as per NFHS-4). Yet, the levels of undernutrition in the state remain high with significant intra-state disparities in nutritional outcomes. It is possible to address undernutrition in the state by scaling-up a set of proven nutrition interventions, which are included in government’s policy framework. However, challenges pertaining to adequacy of funds, issues in fund utilisation and bottlenecks in implementation have affected their coverage in the state.
In this context, Centre for Budget and Governance Accountability (CBGA), in collaboration with UNICEF India, has examined some aspects of public financing for nutrition in Bihar. Based on this research, a set of four policy briefs have been developed which aim to highlight the key findings and associated policy asks emerging from the analysis.

Budgeting for Nutrition-Specific Interventions in Bihar Outlays, Adequacy and Expenditure

Budget Outlays for Nutrition Sensitive Programmes in Bihar

Fiscal Bottlenecks Constraining Delivery of Nutrition Interventions for Pregnant Women in Purnea, Bihar

Challenges in Analysing Public Expenditure for Nutrition in Bihar